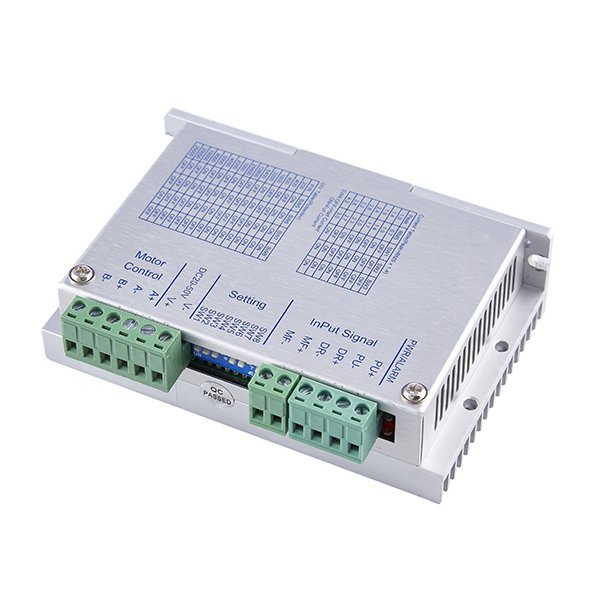
There are significant differences between stepper motors and DC motors in multiple aspects, mainly reflected in control methods, accuracy, speed range, response speed, torque characteristics, cost, control complexity, and application fields.
control mode
Stepper motor: Control its step angle and speed through pulse signals. Every time a pulse signal is input, the rotor rotates a fixed angle or advances one step, so the position and speed of the stepper motor can be precisely adjusted by controlling the number and frequency of pulses.
DC motor: Its speed and torque are controlled by adjusting the voltage or current. Changes in voltage or current directly affect the magnetic field and torque generated by the motor, thereby altering the motor's speed and output torque.
accuracy
Stepper motor: With high precision, it can achieve precise position control. Its output angular displacement or linear displacement is strictly proportional to the number of input pulses, making it excellent in situations where high-precision position control is required.
DC motor: Although it can also achieve a certain degree of position control, its accuracy is usually lower compared to stepper motors.
Speed range
DC motor: With a wide speed range, it can be widely adjusted from low to high speed.
Stepper motor: The speed is usually within a certain range and is limited by the pulse frequency and the performance of the motor itself.
response speed
DC motor: Fast response speed, able to quickly respond to changes in control signals.
Stepper motor: The response speed is relatively slow, especially in situations where frequent starting and stopping are required. Acceleration and deceleration control may be necessary to avoid the occurrence of out of step or over step phenomena.
Torque characteristics
DC motor: It usually has a large torque at low speeds and is suitable for situations that require high torque output.
The torque characteristics of stepper motors may vary depending on the model and design, but generally speaking, their torque may be relatively small at low speeds.
Cost and control complexity
Cost: Generally speaking, the cost of DC motors is relatively low, while the cost of stepper motors is higher. This is mainly due to the relatively complex control system of stepper motors, which requires specialized driving circuits and controllers.
Control complexity: The control of stepper motors is relatively complex, requiring precise control of parameters such as the number, frequency, and phase sequence of pulses. The control of DC motors is relatively simple, mainly achieved by adjusting voltage or current.
application area
Stepper motor: Due to its high precision and ease of digital control, it is widely used in applications that require precise position control, such as automation equipment, robots, CNC machine tools, etc.
DC motor: Due to its wide speed range, fast response speed, and low cost, it is widely used in household appliances, automobiles, mechanical equipment, and other fields, such as electric fans, electric vehicles, and mechanical manufacturing.
In summary, there are significant differences between stepper motors and DC motors in multiple aspects. When choosing a motor, it is necessary to comprehensively evaluate and select the appropriate motor type based on specific application requirements, accuracy requirements, cost considerations, and other factors.