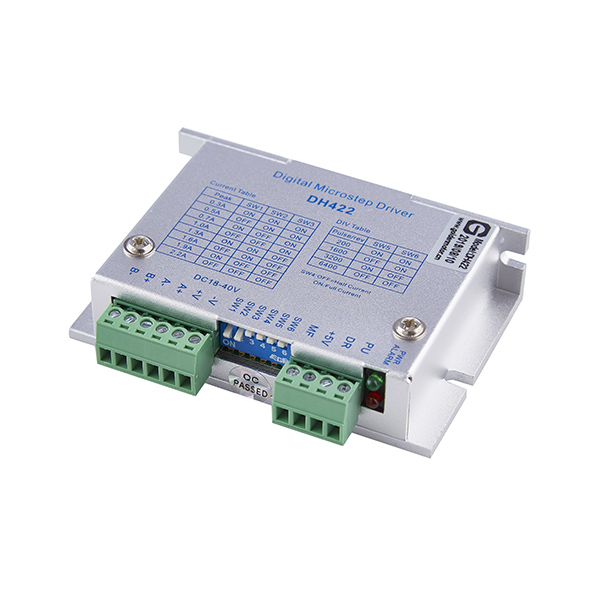
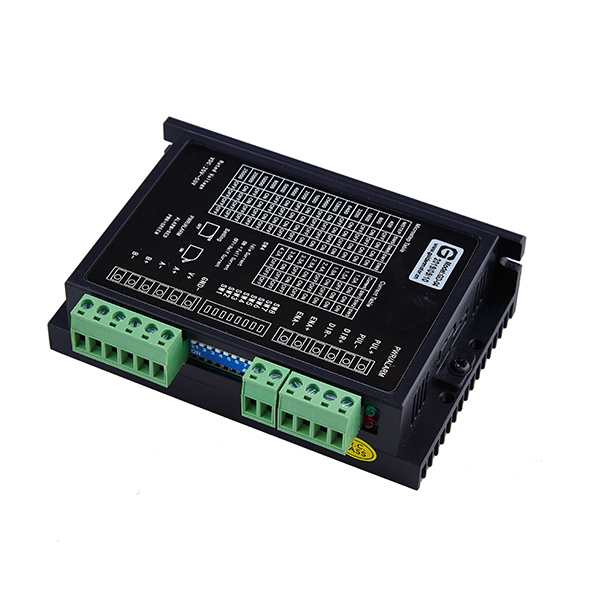
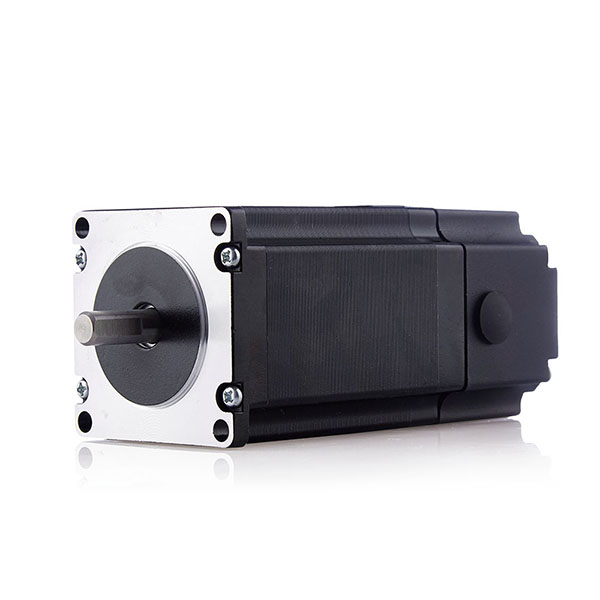
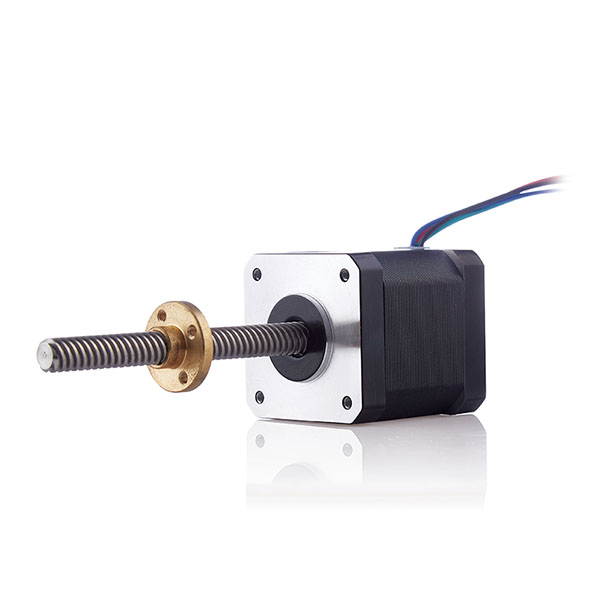
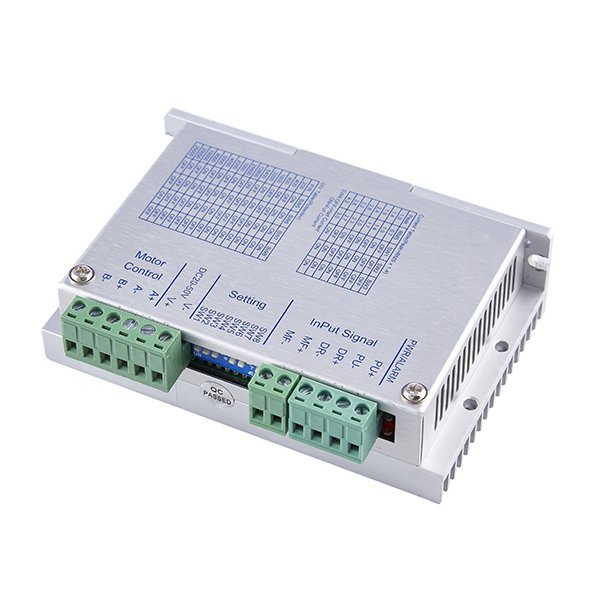
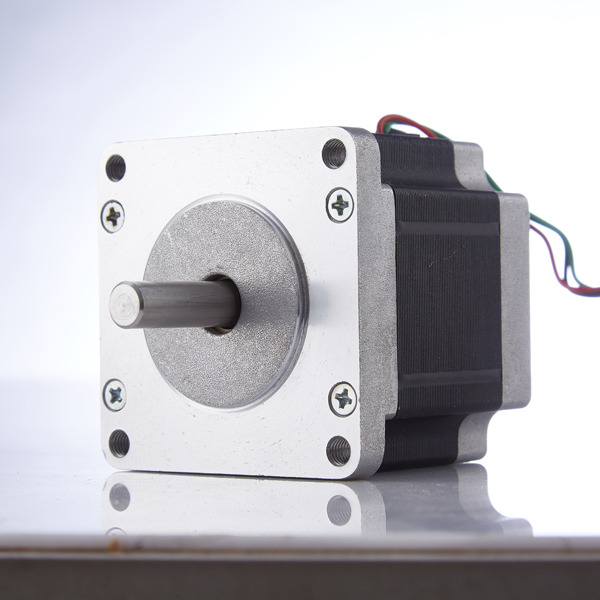
A stepper motor is an open-loop control element that converts electrical pulse signals into angular displacement or linear displacement. The commonly used terms for stepper motors summarized below are:
Step angle: The angle at which the rotor rotates when each electrical pulse signal is input is called the step angle, and the size of the step angle can directly affect the operating accuracy of the motor.
Half step: During single-phase excitation, the motor shaft stops at the full step position. After receiving the next pulse, if the driver excites the other phase and maintains the original phase in the excited state, the motor shaft will move half a basic step angle and stop in the middle of two adjacent full step positions. This cycle applies single-phase and two-phase excitation to the two-phase coils, and the stepper motor will rotate at half a basic step angle per pulse.
Whole step: The most basic driving method, where each pulse of this driving method moves the motor by a basic step angle.
Subdivision: Subdivision refers to the actual step angle of the motor during operation being a fraction of the basic step angle. For example, when the driver operates in a 10 step subdivision state, its step angle is only one tenth of the inherent step angle of the motor. That is to say, when the driver operates in a non subdivision full step state, the control system sends a step pulse and the motor rotates 1.8 °; When using a subdivision driver to operate in the 10 subdivision state, the motor only rotates 0.18 °. The subdivision function is generated by the driver by precisely controlling the phase current of the motor, and is independent of the motor.
Stepper motors have been widely used in various fields, but they cannot be used like ordinary DC motors. AC motors are commonly used and must be controlled by a dual ring pulse signal, power drive circuit, and other components. Therefore, using a good stepper motor is not an easy task. Purchasing a good stepper motor is the first step in using a good stepper motor.